4 changed files with 791 additions and 0 deletions
+ 790
- 0
documentation/articles/AddingJPAToTheAddressBookDemo.asciidoc
View File
| @@ -0,0 +1,790 @@ | |||
| [[adding-jpa-to-the-address-book-demo]] | |||
| Adding JPA to the address book demo | |||
| ----------------------------------- | |||
| Petter Holmström | |||
| [[introduction]] | |||
| Introduction | |||
| ~~~~~~~~~~~~ | |||
| The https://github.com/vaadin/addressbook/tree/v7[Vaading address book] tutorial (the one | |||
| hour version, that is) does a very good job introducing the different | |||
| parts of Vaadin. However, it only uses an in-memory data source with | |||
| randomly generated data. This may be sufficient for demonstration | |||
| purposes, but not for any real world applications that manage data. | |||
| Therefore, in this article, we are going to replace the tutorial's | |||
| in-memory data source with the Java Persistence API (JPA) and also | |||
| utilize some of the new JEE 6 features of | |||
| https://glassfish.dev.java.net/[GlassFish] 3. | |||
| [[prerequisites]] | |||
| Prerequisites | |||
| ^^^^^^^^^^^^^ | |||
| In order to fully understand this article, you should be familiar with | |||
| JEE and JPA development and you should also have read through the Vaadin | |||
| tutorial. | |||
| If you want to try out the code in this article you should get the | |||
| latest version of GlassFish 3 (build 67 was used for this article) and | |||
| http://ant.apache.org[Apache Ant 1.7]. You also need to download the | |||
| https://github.com/eriklumme/doc-attachments/blob/master/attachments/addressbook.tar.gz[source code]. *Note, that you have to edit the | |||
| _build.xml_ file to point to the correct location of the GlassFish | |||
| installation directory before you can use it!* | |||
| [[the-system-architecture]] | |||
| The System Architecture | |||
| ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ | |||
| The architecture of the application is presented in the following | |||
| diagram: | |||
| image:img/architecture2.png[System architecture diagram] | |||
| In addition to the Vaadin UI created in the tutorial, we will add a | |||
| stateless Enterprise Java Bean (EJB) to act as a facade to the database. | |||
| The EJB will in turn use JPA to communicate with a JDBC data source (in | |||
| this example, the built-in `jdbc/sample` data source). | |||
| [[refactoring-the-domain-model]] | |||
| Refactoring the Domain Model | |||
| ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ | |||
| Before doing anything else, we have to modify the domain model of the | |||
| Address Book example. | |||
| [[the-person-class]] | |||
| The Person class | |||
| ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^ | |||
| In order to use JPA, we have to add JPA annotations to the `Person` | |||
| class: | |||
| [source,java] | |||
| .... | |||
| // Imports omitted | |||
| @Entity | |||
| public class Person implements Serializable { | |||
| @Id | |||
| @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY) | |||
| private Long id; | |||
| @Version | |||
| @Column(name = "OPTLOCK") | |||
| private Long version; | |||
| private String firstName = ""; | |||
| private String lastName = ""; | |||
| private String email = ""; | |||
| private String phoneNumber = ""; | |||
| private String streetAddress = ""; | |||
| private Integer postalCode = null; | |||
| private String city = ""; | |||
| public Long getId() { | |||
| return id; | |||
| } | |||
| public Long getVersion() { | |||
| return version; | |||
| } | |||
| // The rest of the methods omitted | |||
| } | |||
| .... | |||
| As we do not need to fit the domain model onto an existing database, the | |||
| annotations become very simple. We have only marked the class as being | |||
| an entity and added an ID and a version field. | |||
| [[the-personreference-class]] | |||
| The PersonReference class | |||
| ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^ | |||
| There are many advantages with using JPA or any other Object Persistence | |||
| Framework (OPF). The underlying database gets completely abstracted away | |||
| and we can work with the domain objects themselves instead of query | |||
| results and records. We can detach domain objects, send them to a client | |||
| using a remote invocation protocol, then reattach them again. | |||
| However, there are a few use cases where using an OPF is not such a good | |||
| idea: reporting and listing. When a report is generated or a list of | |||
| entities is presented to the user, normally only a small part of the | |||
| data is actually required. When the number of objects to fetch is large | |||
| and the domain model is complex, constructing the object graphs from the | |||
| database can be a very lengthy process that puts the users' patience to | |||
| the test – especially if they are only trying to select a person's name | |||
| from a list. | |||
| Many OPFs support lazy loading of some form, where references and | |||
| collections are fetched on demand. However, this rarely works outside | |||
| the container, e.g. on the other side of a remoting connection. | |||
| One way of working around this problem is to let reports and lists | |||
| access the database directly using SQL. This is a fast approach, but it | |||
| also couples the code to a particular SQL dialect and therefore to a | |||
| particular database vendor. | |||
| In this article, we are going to select the road in the middle – we will | |||
| only fetch the property values we need instead of the entire object, but | |||
| we will use PQL and JPA to do so. In this example, this is a slight | |||
| overkill as we have a very simple domain model. However, we do this for | |||
| two reasons: Firstly, as Vaadin is used extensively in business | |||
| applications where the domain models are complex, we want to introduce | |||
| this pattern in an early stage. Secondly, it makes it easier to plug | |||
| into Vaadin's data model. | |||
| In order to implement this pattern, we need to introduce a new class, | |||
| namely `PersonReference`: | |||
| [source,java] | |||
| .... | |||
| import com.vaadin.data.Item; | |||
| import com.vaadin.data.Property; | |||
| import com.vaadin.data.util.ObjectProperty; | |||
| // Some imports omitted | |||
| public class PersonReference implements Serializable, Item { | |||
| private Long personId; | |||
| private Map<Object, Property> propertyMap; | |||
| public PersonReference(Long personId, Map<String, Object> propertyMap) { | |||
| this.personId = personId; | |||
| this.propertyMap = new HashMap<Object, Property>(); | |||
| for (Map.Entry<Object, Property> entry : propertyMap.entrySet()) { | |||
| this.propertyMap.put(entry.getKey(), new ObjectProperty(entry.getValue())); | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| public Long getPersonId() { | |||
| return personId; | |||
| } | |||
| public Property getItemProperty(Object id) { | |||
| return propertyMap.get(id); | |||
| } | |||
| public Collection<?> getItemPropertyIds() { | |||
| return Collections.unmodifiableSet(propertyMap.keySet()); | |||
| } | |||
| public boolean addItemProperty(Object id, Property property) { | |||
| throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Item is read-only."); | |||
| } | |||
| public boolean removeItemProperty(Object id) { | |||
| throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Item is read-only."); | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| .... | |||
| The class contains the ID of the actual `Person` object and a `Map` of | |||
| property values. It also implements the `com.vaadin.data.Item` | |||
| interface, which makes it directly usable in Vaadin's data containers. | |||
| [[the-querymetadata-class]] | |||
| The QueryMetaData class | |||
| ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^ | |||
| Before moving on to the EJB, we have to introduce yet another class, | |||
| namely `QueryMetaData`: | |||
| [source,java] | |||
| .... | |||
| // Imports omitted | |||
| public class QueryMetaData implements Serializable { | |||
| private boolean[] ascending; | |||
| private String[] orderBy; | |||
| private String searchTerm; | |||
| private String propertyName; | |||
| public QueryMetaData(String propertyName, String searchTerm, String[] orderBy, boolean[] ascending) { | |||
| this.propertyName = propertyName; | |||
| this.searchTerm = searchTerm; | |||
| this.ascending = ascending; | |||
| this.orderBy = orderBy; | |||
| } | |||
| public QueryMetaData(String[] orderBy, boolean[] ascending) { | |||
| this(null, null, orderBy, ascending); | |||
| } | |||
| public boolean[] getAscending() { | |||
| return ascending; | |||
| } | |||
| public String[] getOrderBy() { | |||
| return orderBy; | |||
| } | |||
| public String getSearchTerm() { | |||
| return searchTerm; | |||
| } | |||
| public String getPropertyName() { | |||
| return propertyName; | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| .... | |||
| As the class name suggests, this class contains query meta data such as | |||
| ordering and filtering information. We are going to look at how it is | |||
| used in the next section. | |||
| [[the-stateless-ejb]] | |||
| The Stateless EJB | |||
| ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ | |||
| We are now ready to begin designing the EJB. As of JEE 6, an EJB is no | |||
| longer required to have an interface. However, as it is a good idea to | |||
| use interfaces at the boundaries of system components, we will create | |||
| one nonetheless: | |||
| [source,java] | |||
| .... | |||
| // Imports omitted | |||
| @TransactionAttribute | |||
| @Local | |||
| public interface PersonManager { | |||
| public List<PersonReference> getPersonReferences(QueryMetaData queryMetaData, String... propertyNames); | |||
| public Person getPerson(Long id); | |||
| public Person savePerson(Person person); | |||
| } | |||
| .... | |||
| Please note the `@TransactionAttribute` and `@Local` annotations that | |||
| instruct GlassFish to use container managed transaction handling, and to | |||
| use local references, respectively. Next, we create the implementation: | |||
| [source,java] | |||
| .... | |||
| // Imports omitted | |||
| @Stateless | |||
| public class PersonManagerBean implements PersonManager { | |||
| @PersistenceContext | |||
| protected EntityManager entityManager; | |||
| public Person getPerson(Long id) { | |||
| // Implementation omitted | |||
| } | |||
| public List<PersonReference> getPersonReferences(QueryMetaData queryMetaData, String... propertyNames) { | |||
| // Implementation omitted | |||
| } | |||
| public Person savePerson(Person person) { | |||
| // Implementation omitted | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| .... | |||
| We use the `@Stateless` annotation to mark the implementation as a | |||
| stateless session EJB. We also use the `@PersistenceContext` annotation | |||
| to instruct the container to automatically inject the entity manager | |||
| dependency. Thus, we do not have to do any lookups using e.g. JNDI. | |||
| Now we can move on to the method implementations. | |||
| [source,java] | |||
| .... | |||
| public Person getPerson(Long id) { | |||
| return entityManager.find(Person.class, id); | |||
| } | |||
| .... | |||
| This implementation is very straight-forward: given the unique ID, we | |||
| ask the entity manager to look up the corresponding `Person` instance | |||
| and return it. If no such instance is found, `null` is returned. | |||
| [source,java] | |||
| .... | |||
| public List<PersonReference> getPersonReferences(QueryMetaData queryMetaData, String... propertyNames) { | |||
| StringBuffer pqlBuf = new StringBuffer(); | |||
| pqlBuf.append("SELECT p.id"); | |||
| for (int i = 0; i < propertyNames.length; i++) { | |||
| pqlBuf.append(","); | |||
| pqlBuf.append("p."); | |||
| pqlBuf.append(propertyNames[i]); | |||
| } | |||
| pqlBuf.append(" FROM Person p"); | |||
| if (queryMetaData.getPropertyName() != null) { | |||
| pqlBuf.append(" WHERE p."); | |||
| pqlBuf.append(queryMetaData.getPropertyName()); | |||
| if (queryMetaData.getSearchTerm() == null) { | |||
| pqlBuf.append(" IS NULL"); | |||
| } else { | |||
| pqlBuf.append(" = :searchTerm"); | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| if (queryMetaData != null && queryMetaData.getAscending().length > 0) { | |||
| pqlBuf.append(" ORDER BY "); | |||
| for (int i = 0; i < queryMetaData.getAscending().length; i++) { | |||
| if (i > 0) { | |||
| pqlBuf.append(","); | |||
| } | |||
| pqlBuf.append("p."); | |||
| pqlBuf.append(queryMetaData.getOrderBy()[i]); | |||
| if (!queryMetaData.getAscending()[i]) { | |||
| pqlBuf.append(" DESC"); | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| String pql = pqlBuf.toString(); | |||
| Query query = entityManager.createQuery(pql); | |||
| if (queryMetaData.getPropertyName() != null && queryMetaData.getSearchTerm() != null) { | |||
| query.setParameter("searchTerm", queryMetaData.getSearchTerm()); | |||
| } | |||
| List<Object[]> result = query.getResultList(); | |||
| List<PersonReference> referenceList = new ArrayList<PersonReference>(result.size()); | |||
| HashMap<String, Object> valueMap; | |||
| for (Object[] row : result) { | |||
| valueMap = new HashMap<String, Object>(); | |||
| for (int i = 1; i < row.length; i++) { | |||
| valueMap.put(propertyNames[i - 1], row[i]); | |||
| } | |||
| referenceList.add(new PersonReference((Long) row[0], valueMap)); | |||
| } | |||
| return referenceList; | |||
| } | |||
| .... | |||
| This method is a little more complicated and also demonstrates the usage | |||
| of the `QueryMetaData` class. What this method does is that it | |||
| constructs a PQL query that fetches the values of the properties | |||
| provided in the `propertyNames` array from the database. It then uses | |||
| the `QueryMetaData` instance to add information about ordering and | |||
| filtering. Finally, it executes the query and returns the result as a | |||
| list of `PersonReference` instances. | |||
| The advantage with using `QueryMetaData` is that additional query | |||
| options can be added without having to change the interface. We could | |||
| e.g. create a subclass named `AdvancedQueryMetaData` with information | |||
| about wildcards, result size limitations, etc. | |||
| [source,java] | |||
| .... | |||
| public Person savePerson(Person person) { | |||
| if (person.getId() == null) | |||
| entityManager.persist(person); | |||
| else | |||
| entityManager.merge(person); | |||
| return person; | |||
| } | |||
| .... | |||
| This method checks if `person` is persistent or transient, merges or | |||
| persists it, respectively, and finally returns it. The reason why | |||
| `person` is returned is that this makes the method usable for remote | |||
| method calls. However, as this example does not need any remoting, we | |||
| are not going to discuss this matter any further in this article. | |||
| [[plugging-into-the-ui]] | |||
| Plugging Into the UI | |||
| ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ | |||
| The persistence component of our Address Book application is now | |||
| completed. Now we just have to plug it into the existing user interface | |||
| component. In this article, we are only going to look at some of the | |||
| changes that have to be made to the code. That is, if you try to deploy | |||
| the application with the changes presented in this article only, it will | |||
| not work. For all the changes, please check the source code archive | |||
| attached to this article. | |||
| [[creating-a-new-container]] | |||
| Creating a New Container | |||
| ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^ | |||
| First of all, we have to create a Vaadin container that knows how to | |||
| read data from a `PersonManager`: | |||
| [source,java] | |||
| .... | |||
| // Imports omitted | |||
| public class PersonReferenceContainer implements Container, Container.ItemSetChangeNotifier { | |||
| public static final Object[] NATURAL_COL_ORDER = new String[] {"firstName", "lastName", "email", | |||
| "phoneNumber", "streetAddress", "postalCode", "city"}; | |||
| protected static final Collection<Object> NATURAL_COL_ORDER_COLL = Collections.unmodifiableList( | |||
| Arrays.asList(NATURAL_COL_ORDER) | |||
| ); | |||
| protected final PersonManager personManager; | |||
| protected List<PersonReference> personReferences; | |||
| protected Map<Object, PersonReference> idIndex; | |||
| public static QueryMetaData defaultQueryMetaData = new QueryMetaData( | |||
| new String[]{"firstName", "lastName"}, new boolean[]{true, true}); | |||
| protected QueryMetaData queryMetaData = defaultQueryMetaData; | |||
| // Some fields omitted | |||
| public PersonReferenceContainer(PersonManager personManager) { | |||
| this.personManager = personManager; | |||
| } | |||
| public void refresh() { | |||
| refresh(queryMetaData); | |||
| } | |||
| public void refresh(QueryMetaData queryMetaData) { | |||
| this.queryMetaData = queryMetaData; | |||
| personReferences = personManager.getPersonReferences(queryMetaData, (String[]) NATURAL_COL_ORDER); | |||
| idIndex = new HashMap<Object, PersonReference>(personReferences.size()); | |||
| for (PersonReference pf : personReferences) { | |||
| idIndex.put(pf.getPersonId(), pf); | |||
| } | |||
| notifyListeners(); | |||
| } | |||
| public QueryMetaData getQueryMetaData() { | |||
| return queryMetaData; | |||
| } | |||
| public void close() { | |||
| if (personReferences != null) { | |||
| personReferences.clear(); | |||
| personReferences = null; | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| public boolean isOpen() { | |||
| return personReferences != null; | |||
| } | |||
| public int size() { | |||
| return personReferences == null ? 0 : personReferences.size(); | |||
| } | |||
| public Item getItem(Object itemId) { | |||
| return idIndex.get(itemId); | |||
| } | |||
| public Collection<?> getContainerPropertyIds() { | |||
| return NATURAL_COL_ORDER_COLL; | |||
| } | |||
| public Collection<?> getItemIds() { | |||
| return Collections.unmodifiableSet(idIndex.keySet()); | |||
| } | |||
| public List<PersonReference> getItems() { | |||
| return Collections.unmodifiableList(personReferences); | |||
| } | |||
| public Property getContainerProperty(Object itemId, Object propertyId) { | |||
| Item item = idIndex.get(itemId); | |||
| if (item != null) { | |||
| return item.getItemProperty(propertyId); | |||
| } | |||
| return null; | |||
| } | |||
| public Class<?> getType(Object propertyId) { | |||
| try { | |||
| PropertyDescriptor pd = new PropertyDescriptor((String) propertyId, Person.class); | |||
| return pd.getPropertyType(); | |||
| } catch (Exception e) { | |||
| return null; | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| public boolean containsId(Object itemId) { | |||
| return idIndex.containsKey(itemId); | |||
| } | |||
| // Unsupported methods omitted | |||
| // addListener(..) and removeListener(..) omitted | |||
| protected void notifyListeners() { | |||
| ArrayList<ItemSetChangeListener> cl = (ArrayList<ItemSetChangeListener>) listeners.clone(); | |||
| ItemSetChangeEvent event = new ItemSetChangeEvent() { | |||
| public Container getContainer() { | |||
| return PersonReferenceContainer.this; | |||
| } | |||
| }; | |||
| for (ItemSetChangeListener listener : cl) { | |||
| listener.containerItemSetChange(event); | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| .... | |||
| Upon creation, this container is empty. When one of the `refresh(..)` | |||
| methods is called, a list of `PersonReference`s are fetched from the | |||
| `PersonManager` and cached locally. Even though the database is updated, | |||
| e.g. by another user, the container contents will not change before the | |||
| next call to `refresh(..)`. | |||
| To keep things simple, the container is read only, meaning that all | |||
| methods that are designed to alter the contents of the container throw | |||
| an exception. Sorting, optimization and lazy loading has also been left | |||
| out (if you like, you can try to implement these yourself). | |||
| [[modifying-the-personform-class]] | |||
| Modifying the PersonForm class | |||
| ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^ | |||
| We now have to refactor the code to use our new container, starting with | |||
| the `PersonForm` class. We begin with the part of the constructor that | |||
| creates a list of all the cities currently in the container: | |||
| [source,java] | |||
| .... | |||
| PersonReferenceContainer ds = app.getDataSource(); | |||
| for (PersonReference pf : ds.getItems()) { | |||
| String city = (String) pf.getItemProperty("city").getValue(); | |||
| cities.addItem(city); | |||
| } | |||
| .... | |||
| We have changed the code to iterate a collection of `PersonReference` | |||
| instances instead of `Person` instances. | |||
| Then, we will continue with the part of the `buttonClick(..)` method | |||
| that saves the contact: | |||
| [source,java] | |||
| .... | |||
| if (source == save) { | |||
| if (!isValid()) { | |||
| return; | |||
| } | |||
| commit(); | |||
| person = app.getPersonManager().savePerson(person); | |||
| setItemDataSource(new BeanItem(person)); | |||
| newContactMode = false; | |||
| app.getDataSource().refresh(); | |||
| setReadOnly(true); | |||
| } | |||
| .... | |||
| The code has actually become simpler, as the same method is used to save | |||
| both new and existing contacts. When the contact is saved, the container | |||
| is refreshed so that the new information is displayed in the table. | |||
| Finally, we will add a new method, `editContact(..)` for displaying and | |||
| editing existing contacts: | |||
| [source,java] | |||
| .... | |||
| public void editContact(Person person) { | |||
| this.person = person; | |||
| setItemDataSource(new BeanItem(person)) | |||
| newContactMode = false; | |||
| setReadOnly(true); | |||
| } | |||
| .... | |||
| This method is almost equal to `addContact()` but uses an existing | |||
| `Person` instance instead of a newly created one. It also makes the form | |||
| read only, as the user is expected to click an Edit button to make the | |||
| form editable. | |||
| [[modifying-the-addressbookapplication-class]] | |||
| Modifying the AddressBookApplication class | |||
| ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^ | |||
| Finally, we are going to replace the old container with the new one in | |||
| the main application class. We will start by adding a constructor: | |||
| [source,java] | |||
| .... | |||
| public AddressBookApplication(PersonManager personManager) { | |||
| this.personManager = personManager; | |||
| } | |||
| .... | |||
| This constructor will be used by a custom application servlet to inject | |||
| a reference to the `PersonManager` EJB. When this is done, we move on to | |||
| the `init()` method: | |||
| [source,java] | |||
| .... | |||
| public void init() { | |||
| dataSource = new PersonReferenceContainer(personManager); | |||
| dataSource.refresh(); // Load initial data | |||
| buildMainLayout(); | |||
| setMainComponent(getListView()); | |||
| } | |||
| .... | |||
| The method creates a container and refreshes it in order to load the | |||
| existing data from the database – otherwise, the user would be presented | |||
| with an empty table upon application startup. | |||
| Next, we modify the code that is used to select contacts: | |||
| [source,java] | |||
| .... | |||
| public void valueChange(ValueChangeEvent event) { | |||
| Property property = event.getProperty(); | |||
| if (property == personList) { | |||
| Person person = personManager.getPerson((Long) personList.getValue()); | |||
| personForm.editContact(person); | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| .... | |||
| The method gets the ID of the currently selected person and uses it to | |||
| lookup the `Person` instance from the database, which is then passed to | |||
| the person form using the newly created `editContact(..)` method. | |||
| Next, we modify the code that handles searches: | |||
| [source,java] | |||
| .... | |||
| public void search(SearchFilter searchFilter) { | |||
| QueryMetaData qmd = new QueryMetaData((String) searchFilter.getPropertyId(), searchFilter.getTerm(), | |||
| getDataSource().getQueryMetaData().getOrderBy(), | |||
| getDataSource().getQueryMetaData().getAscending()); | |||
| getDataSource().refresh(qmd); | |||
| showListView(); | |||
| // Visual notification omitted | |||
| } | |||
| .... | |||
| Instead of filtering the container, this method constructs a new | |||
| `QueryMetaData` instance and refreshes the data source. Thus, the search | |||
| operation is performed in the database and not in the container itself. | |||
| As we have removed container filtering, we also have to change the code | |||
| that is used to show all contacts: | |||
| [source,java] | |||
| .... | |||
| public void itemClick(ItemClickEvent event) { | |||
| if (event.getSource() == tree) { | |||
| Object itemId = event.getItemId(); | |||
| if (itemId != null) { | |||
| if (itemId == NavigationTree.SHOW_ALL) { | |||
| getDataSource().refresh(PersonReferenceContainer.defaultQueryMetaData); | |||
| showListView(); | |||
| } else if (itemId == NavigationTree.SEARCH) { | |||
| showSearchView(); | |||
| } else if (itemId instanceof SearchFilter) { | |||
| search((SearchFilter) itemId); | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| .... | |||
| Instead of removing the filters, this method refreshes the data source | |||
| using the default query meta data. | |||
| [[creating-a-custom-servlet]] | |||
| Creating a Custom Servlet | |||
| ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ | |||
| The original tutorial used an `ApplicationServlet` configured in | |||
| _web.xml_ to start the application. In this version, however, we are | |||
| going to create our own custom servlet. By doing this, we can let | |||
| GlassFish inject the reference to the `PersonManager` EJB using | |||
| annotations, which means that we do not need any JDNI look ups at all. | |||
| As a bonus, we get rid of the _web.xml_ file as well thanks to the new | |||
| JEE 6 `@WebServlet` annotation. The servlet class can be added as an | |||
| inner class to the main application class: | |||
| [source,java] | |||
| .... | |||
| @WebServlet(urlPatterns = "/*") | |||
| public static class Servlet extends AbstractApplicationServlet { | |||
| @EJB | |||
| PersonManager personManager; | |||
| @Override | |||
| protected Application getNewApplication(HttpServletRequest request) throws ServletException { | |||
| return new AddressBookApplication(personManager); | |||
| } | |||
| @Override | |||
| protected Class<? extends Application> getApplicationClass() throws ClassNotFoundException { | |||
| return AddressBookApplication.class; | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| .... | |||
| When the servlet is initialized by the web container, the | |||
| `PersonManager` EJB will be automatically injected into the | |||
| `personManager` field thanks to the `@EJB` annotation. This reference | |||
| can then be passed to the main application class in the | |||
| `getNewApplication(..)` method. | |||
| [[classical-deployment]] | |||
| Classical Deployment | |||
| ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ | |||
| Packaging this application into a WAR is no different from the Hello | |||
| World example. We just have to remember to include the _persistence.xml_ | |||
| file (we are not going to cover the contents of this file in this | |||
| article), otherwise JPA will not work. Note, that as of JEE 6, we do not | |||
| need to split up the application into a different bundle for the EJB and | |||
| another for the UI. We also do not need any other configuration files | |||
| than the persistence unit configuration file. | |||
| The actual packaging can be done using the following Ant target: | |||
| [source,xml] | |||
| .... | |||
| <target name="package-with-vaadin" depends="compile"> | |||
| <mkdir dir="${dist.dir}"/> | |||
| <war destfile="${dist.dir}/${ant.project.name}-with-vaadin.war" needxmlfile="false"> | |||
| <lib file="${vaadin.jar}"/> | |||
| <classes dir="${build.dir}"/> | |||
| <fileset dir="${web.dir}" includes="**"/> | |||
| </war> | |||
| </target> | |||
| .... | |||
| Once the application has been packaged, it can be deployed like so, | |||
| using the *asadmin* tool that comes with GlassFish: | |||
| [source,bash] | |||
| .... | |||
| $ asadmin deploy /path/to/addressbook-with-vaadin.war | |||
| .... | |||
| Note, that the Java DB database bundled with GlassFish must be started | |||
| prior to deploying the application. Now we can test the application by | |||
| opening a web browser and navigating to | |||
| http://localhost:8080/addressbook-with-vaadin. The running application | |||
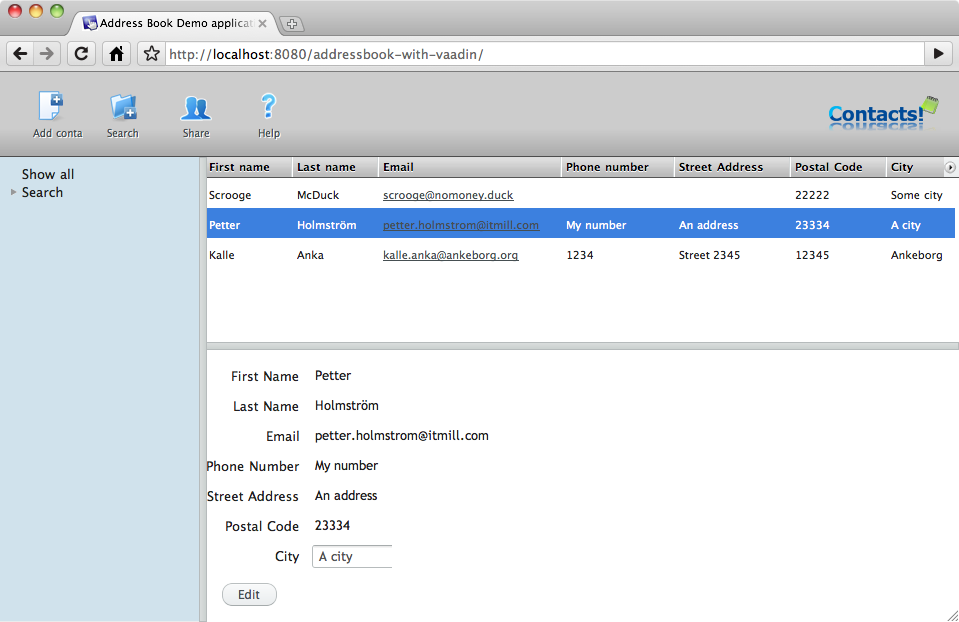
| should look something like this: | |||
| image:img/ab-with-vaadin-scrshot.png[Running application screenshot] | |||
| [[osgi-deployment-options]] | |||
| OSGi Deployment Options | |||
| ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ | |||
| The OSGi support of GlassFish 3 introduces some new possibilities for | |||
| Vaadin development. If the Vaadin library is deployed as an OSGi bundle, we can package and | |||
| deploy the address book application without the Vaadin library. The | |||
| following Ant target can be used to create the WAR: | |||
| [source,xml] | |||
| .... | |||
| <target name="package-without-vaadin" depends="compile"> | |||
| <mkdir dir="${dist.dir}"/> | |||
| <war destfile="${dist.dir}/${ant.project.name}-without-vaadin.war" needxmlfile="false"> | |||
| <classes dir="${build.dir}"/> | |||
| <fileset dir="${web.dir}" includes="**"/> | |||
| </war> | |||
| </target> | |||
| .... | |||
| [[summary]] | |||
| Summary | |||
| ~~~~~~~ | |||
| In this article, we have extended the Address Book demo to use JPA | |||
| instead of the in-memory container, with an EJB acting as the facade to | |||
| the database. Thanks to annotations, the application does not contain a | |||
| single JNDI lookup, and thanks to JEE 6, the application can be deployed | |||
| as a single WAR. | |||
+ 1
- 0
documentation/articles/contents.asciidoc
View File
| @@ -18,3 +18,4 @@ | |||
| - link:UsingPhoneGapBuildWithVaadinTouchKit.asciidoc[Using PhoneGap Build with Vaadin TouchKit] | |||
| - link:ScalaAndVaadinHOWTO.asciidoc[Scala and Vaadin how-to] | |||
| - link:UsingHibernateWithVaadin.asciidoc[Using Hibernate with Vaadin] | |||
| - link:AddingJPAToTheAddressBookDemo.asciidoc[Adding JPA to the address book demo] | |||
BIN
documentation/articles/img/ab-with-vaadin-scrshot.png
View File
BIN
documentation/articles/img/architecture2.png
View File

Loading…
