2.5 KiB
Rspamd user settings
Table of Contents
Introduction
Rspamd allows to specify custom settings according to incoming messages. Each setting define some set of custom metric weights, symbols or actions. An administrator can also skip spam checks for certain messages completely. Rspamd settings can be loaded as dynamic map and updated automatically if a corresponding file or URL has changed since last update.
To load settings as dynamic map, you can set 'settings' to a map string:
settings = "http://host/url"
If you don't want dynamic updates then you can set settings to an object:
settings {
setting1 = {
...
}
setting2 = {
...
}
}
Settings structure
The settings file itself should contain a single section called "settings":
settings {
some_users {
priority = high;
from = "@example.com";
rcpt = "admin";
rcpt = "/user.*/";
ip = "172.16.0.0/16";
user = "@example.net";
apply "default" {
symbol1 = 10.0;
symbol2 = 0.0;
actions {
reject = 100.0
greylist = 10.0
}
}
}
whitelist {
priority = low;
rcpt = "postmaster@example.com";
want_spam = yes;
}
}
So each setting has the following attributes:
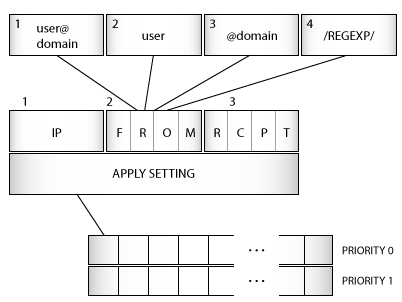
name- section name that identify this specific setting (e.g.some_users)priority- high or low, high priority rules are matched first (default priority is low)match list- list of rules when this rule matches:from- match SMTP fromrcpt- match RCPTip- match source IP addressuser- matches authenticated user ID of message sender if any
apply- list of applied rules, identified by metric name (e.g.default)symbol- modify weight of a symbolactions- section of modified actions
Match section performs AND operation on different matches, for example, if you have
from and rcpt in the same rule, then rule matches only when from AND rcpt match.
For the same matches OR rule applies. Therefore, if you have multiple rcpt matches, then any of
these rcpt will trigger the rule. If a setting applies no more rules are matched.
Regexp rules are slow and should not be used intensively. All other rules are matched fast enough.
The picture below describes the architecture of settings matching.